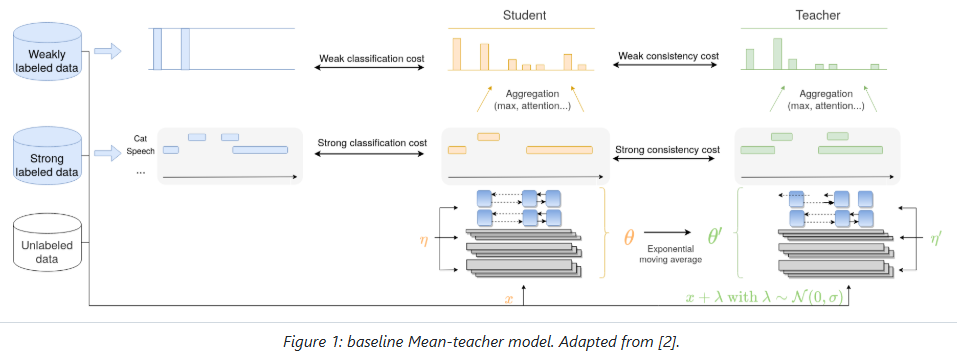
Data Preprocessing
_get_logits_one_head
def _get_logits_one_head(
self, x, pad_mask, dense, dense_softmax, classes_mask=None
):
strong = dense(x) # [bs, frames, nclass]
strong = self.sigmoid(strong)
if classes_mask is not None:
classes_mask = ~classes_mask[:, None].expand_as(strong)
if self.attention in [True, "legacy"]:
sof = dense_softmax(x) # [bs, frames, nclass]
if not pad_mask is None:
sof = sof.masked_fill(pad_mask.transpose(1, 2), -1e30) # mask attention
if classes_mask is not None:
# mask the invalid classes, cannot attend to these
sof = sof.masked_fill(classes_mask, -1e30)
sof = self.softmax(sof)
sof = torch.clamp(sof, min=1e-7, max=1)
weak = (strong * sof).sum(1) / sof.sum(1) # [bs, nclass]
else:
weak = strong.mean(1)
if classes_mask is not None:
# mask invalid
strong = strong.masked_fill(classes_mask, 0.0)
weak = weak.masked_fill(classes_mask[:, 0], 0.0)
return strong.transpose(1, 2), weak #[bs, nclass, frames], [bs, nclass]강력한(Strong) 예측: 각 시간 프레임마다 소리 이벤트가 있는지 예측
- 입력 특징(x)에 밀집층(dense)을 적용해 각 프레임별 각 클래스의 점수를 계산
- 시그모이드 함수를 적용해 0~1 사이 값으로 변환
약한(Weak) 예측: 전체 오디오 클립에 소리 이벤트가 있는지만 예측
- 강력한 예측과 어텐션 가중치를 곱한 후 합산하여 가중 평균을 계산
- attention 사용 x : 단순히 모든 프레임의 강력한 예측 평균을 계산
마스킹 처리 : 유효하지 않은 클래스가 있으면 해당 예측을 0으로 설정
Example
weak : [0.8, 0.2, 0.0, 0.95] 첫 번째와 네 번째 소리 유형이 높은 확률로 존재
strong =[[[0.1, 0.2, 0.8, 0.9, 0.7], # 첫 번째 클래스(개 짖는 소리)
[0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.0], # 두 번째 클래스(자동차 경적)
[0.3, 0.2, 0.1, 0.0, 0.0]]] # 세 번째 클래스(사이렌)_get_logits
다중 헤드 :
- nclass가 여러 개이면
- 여러 번 _get_logits_one_head 호출
- 클래스 차원을 기준으로 펼쳐서 가중치 반환
단일 헤드:
- nclass가 여러 개가 아니라 하나면
-_get_logits_one_head 함수로 동작 후 반환
def _get_logits(self, x, pad_mask, classes_mask=None):
out_strong = []
out_weak = []
if isinstance(self.nclass, (tuple, list)):
# instead of masking the softmax we can have multiple heads for each dataset:
# maestro_synth, maestro_real and desed.
# not sure which approach is better. We must try.
for indx, c_classes in enumerate(self.nclass):
dense_softmax = (
self.dense_softmax[indx] if hasattr(self, "dense_softmax") else None
)
c_strong, c_weak = self._get_logits_one_head(
x, pad_mask, self.dense[indx], dense_softmax, classes_mask
)
out_strong.append(c_strong)
out_weak.append(c_weak)
# concatenate over class dimension
return torch.cat(out_strong, 1), torch.cat(out_weak, 1)
else:
dense_softmax = (
self.dense_softmax if hasattr(self, "dense_softmax") else None
)
return self._get_logits_one_head(
x, pad_mask, self.dense, dense_softmax, classes_mask
)apply_specaugment -데이터 증강(data augmentation)
def apply_specaugment(self, x):
if self.training:
timemask = torchaudio.transforms.TimeMasking(
self.specaugm_t_l, True, self.specaugm_t_p
)
freqmask = torchaudio.transforms.TimeMasking(
self.specaugm_f_l, True, self.specaugm_f_p
) # use time masking also here
x = timemask(freqmask(x.transpose(1, -1)).transpose(1, -1))
return x훈련 중일 때 두 마스킹을 연속으로 적용
- 잡음이 섞이거나 일부 주파수가 손실된 실제 상황에서도 잘 작동
- 주파수 마스킹 → 시간 마스킹 -> return x
(SpecAugment: A Simple Data Augmentation Method for Automatic Speech Recognition)
Ex) 입력 x: (1, 4, 5) (배치 크기 1, fequency bin 4, frame 5).
forward
def forward(self, x, pad_mask=None, embeddings=None, classes_mask=None):
x = self.apply_specaugment(x)
x = x.transpose(1, 2).unsqueeze(1)
# input size : (batch_size, n_channels, n_frames, n_freq)
if self.cnn_integration:
bs_in, nc_in = x.size(0), x.size(1)
x = x.view(bs_in * nc_in, 1, *x.shape[2:])
# conv features
x = self.cnn(x)
bs, chan, frames, freq = x.size()
if self.cnn_integration:
x = x.reshape(bs_in, chan * nc_in, frames, freq)
if freq != 1:
warnings.warn(
f"Output shape is: {(bs, frames, chan * freq)}, from {freq} staying freq"
)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
x = x.contiguous().view(bs, frames, chan * freq)
else:
x = x.squeeze(-1)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) # [bs, frames, chan]
# rnn features
if self.use_embeddings:
if self.aggregation_type == "global":
x = self.cat_tf(
torch.cat(
(
x,
self.shrink_emb(embeddings)
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, x.shape[1], 1),
),
-1,
)
)
elif self.aggregation_type == "frame":
# there can be some mismatch between seq length of cnn of crnn and the pretrained embeddings, we use an rnn
# as an encoder and we use the last state
last, _ = self.frame_embs_encoder(embeddings.transpose(1, 2))
embeddings = last[:, -1]
reshape_emb = (
self.shrink_emb(embeddings).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, x.shape[1], 1)
)
elif self.aggregation_type == "interpolate":
output_shape = (embeddings.shape[1], x.shape[1])
reshape_emb = (
torch.nn.functional.interpolate(
embeddings.unsqueeze(1), size=output_shape, mode="nearest-exact"
)
.squeeze(1)
.transpose(1, 2)
)
elif self.aggregation_type == "pool1d":
reshape_emb = torch.nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool1d(
embeddings, x.shape[1]
).transpose(1, 2)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
if self.use_embeddings:
if self.dropstep_recurrent and self.training:
dropstep = torchaudio.transforms.TimeMasking(
self.dropstep_recurrent_len, True, self.dropstep_recurrent
)
x = dropstep(x.transpose(1, -1)).transpose(1, -1)
reshape_emb = dropstep(reshape_emb.transpose(1, -1)).transpose(1, -1)
x = self.cat_tf(self.dropout(torch.cat((x, reshape_emb), -1)))
else:
if self.dropstep_recurrent and self.training:
dropstep = torchaudio.transforms.TimeMasking(
self.dropstep_recurrent_len, True, self.dropstep_recurrent
)
x = dropstep(x.transpose(1, 2)).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.rnn(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
return self._get_logits(x, pad_mask, classes_mask)
입력 변환
- SpecAugment 적용 (데이터 증강)
- 차원 변환하여 CNN 입력 형식으로 변환
CNN 처리
- 시간 및 주파수 특징 추출
- 차원 정리하여 RNN 입력으로 변환
Embeddings 추가 (선택)
- 글로벌 / 프레임 기반 / 보간 / 풀링 방식으로 결합
Dropstep 적용 (선택)
- TimeMasking을 적용하여 일반화 성능 향상
RNN 처리
- 시간 흐름을 고려한 특징 학습
- Dropout 적용하여 과적합 방지
최종 출력
- 로짓(logits) 반환 (소프트맥스나 시그모이드로 변환 가능)
Train
def train(self, mode=True):
super(CRNN, self).train(mode)
if self.freeze_bn:
print("Freezing Mean/Var of BatchNorm2D.")
if self.freeze_bn:
print("Freezing Weight/Bias of BatchNorm2D.")
if self.freeze_bn:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.eval()
if self.freeze_bn:
m.weight.requires_grad = False
m.bias.requires_grad = False참고문헌
'AI > MachineLearning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [NLP] 임베딩(Embedding) (0) | 2025.02.27 |
|---|
